| OVERVIEW Labral tears of the shoulder have been a particular focus of attention since the advent of the arthroscope, a small instrument that allows the orthopaedic surgeon to clearly see inside the shoulder joint and view the labrum, its environment, and any injuries that may have occurred. The arthroscope, in conjunction with anatomic dissections, history, physical examination, and symptoms has allowed orthopaedic surgeons to better understand and treat a variety of injuries to the labrum. What does the inside of the shoulder look like? The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the human body. It consists of a complex arrangement of structures working together to provide the movement necessary for daily life. Unfortunately, this great mobility comes at the expense of stability. Four bones and a network of soft tissue structures (ligaments, tendons, and muscles) work together to produce shoulder movement. They interact to keep the joint in place while it moves through extreme ranges of motion. Each of these structures makes an important contribution to shoulder movement and stability. Certain work or sports activities can put great demands upon the shoulder, and injury can occur when the limits of movement are exceeded and/or the individual structures are overloaded. Click here to read more about shoulder structure. What is the labrum and what does it do? The labrum is a disk of cartilage on the glenoid, or "socket" side of the shoulder joint. The labrum helps stabilize 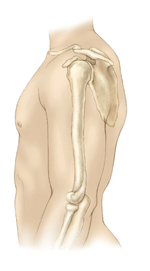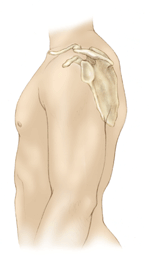 the joint and acts as a "bumper" to limit excessive motion of the humerus, the "ball" side of the shoulder joint. More importantly, it holds the humerus securely to the glenoid, almost as if suction were involved. Although the glenoid itself is a relatively flat surface, the labrum's cuff-like contour gives the glenoid a more concave shape. The secure but flexible fit of the humerus within the glenoid permits the great range motion of the healthy shoulder. the joint and acts as a "bumper" to limit excessive motion of the humerus, the "ball" side of the shoulder joint. More importantly, it holds the humerus securely to the glenoid, almost as if suction were involved. Although the glenoid itself is a relatively flat surface, the labrum's cuff-like contour gives the glenoid a more concave shape. The secure but flexible fit of the humerus within the glenoid permits the great range motion of the healthy shoulder.How is the labrum injured? Tears of the labrum can be the result of:
At least five types of SLAP tears have been identified. Treatment depends on the stability of the biceps anchor and the type of tear that has occurred. These injuries are commonly the result of:
|
SYMPTOMS
The primary symptom of a labral tear that is not associated with instability is pain in the area of the injury. Patients often say:
Patients with labral tears from internal impingement (a pinching of the soft tissues) will complain that they have pain with throwing. Usually the pain is worst when the arm changes direction from late cocking to forward acceleration. In the shoulder, this pain is located posterior (behind) and superior (above). If there is a related partial thickness rotator cuff tear, there may also be lateral (on the side) pain.
The primary symptom of a labral tear that is not associated with instability is pain in the area of the injury. Patients often say:
- the pain is located at the back on top of the shoulder or in the front on top of the shoulder.
- the pain feels like it is deep inside.
- palpation (pressing) on the shoulder does not duplicate the pain that they have.
Patients with labral tears from internal impingement (a pinching of the soft tissues) will complain that they have pain with throwing. Usually the pain is worst when the arm changes direction from late cocking to forward acceleration. In the shoulder, this pain is located posterior (behind) and superior (above). If there is a related partial thickness rotator cuff tear, there may also be lateral (on the side) pain.
DIAGNOSIS
The physician will first take a history of the patient's injury in order to learn how it occurred. As mentioned earlier, the pain from a labral tear is located at the site of the injury, and is usually referred to as being deep inside the shoulder. A thorough physical exam may reveal other sources of injury or another disorder. During a physical examination of the shoulder:
The confirming test for a labral tear is an MRI preceded by an arthrogram. This procedure greatly enhances the diagnostic accuracy by allowing tears of the labrum to be seen more clearly.
- the physician will measure motion to reveal any stiffness, which can be a sign of a labral tear.
- an instability exam will be performed.
- the O'Brien's test which focuses on the biceps and reveals pain, can help diagnose a labral tear.
The confirming test for a labral tear is an MRI preceded by an arthrogram. This procedure greatly enhances the diagnostic accuracy by allowing tears of the labrum to be seen more clearly.
TREATMENT
Non-operative Treatment for Labral Tears
There are probably a large number of untreated labral tears that heal spontaneously since the labrum has a rich blood supply that helps the healing process (except in the anterior and superior locations).
Physical therapy is helpful for certain cases such as internal impingement, in which the rotator cuff rubs the posterior labrum. Physical therapy options include:
Tears that need treatment are usually seen in the chronic stage when spontaneous healing has not occurred. Tears of the biceps tendon anchor are unlikely to heal without treatment because the biceps constantly pulls on the labrum.
Chronic tears may require surgery if patients are unwilling or unable to modify their activities sufficiently to allow for healing and comfort. Surgery should be considered if:
Arthroscopic treatment is the standard of practice for most labral injuries not associated with instability. The majority of these can be treated with simple debridement (removal of abnormal, damaged, or excess tissue). This procedure will eliminate flaps that may impinge the movement of the humerus on the glenoid and/or remove any unstable portion of the labrum.
Certain painful and unstable SLAP tears, in which the biceps is detached, need special attention. If the biceps tendon anchor is no longer firmly attached to the glenoid, it must be re-attached to the bone. The surgeon uses suture anchors and /or arthroscopic knot tying techniques to repair the torn labrum of younger patients.
It is often safer for older individuals to have a debridement of the labrum and a biceps tenodesis. A tenodesis is a procedure in which the biceps is repaired to the bone outside the glenohumeral joint to relieve pain, yet allow it to retain some strength and function. This procedure can be a good choice for older patients because the blood supply to the labrum diminishes with age, making the healing process more difficult. The decision to perform a tenodesis repair should be made by the doctor and patient together, after a thorough discussion of the surgical options and the healing process.
What types of complications can occur?
Complications associated with surgery for labral tears are few:
There are probably a large number of untreated labral tears that heal spontaneously since the labrum has a rich blood supply that helps the healing process (except in the anterior and superior locations).
Physical therapy is helpful for certain cases such as internal impingement, in which the rotator cuff rubs the posterior labrum. Physical therapy options include:
- changing the throwing mechanism.
- strengthening muscles that externally rotate the shoulder.
- stretching the posterior capsule with the help of a physical therapist.
Tears that need treatment are usually seen in the chronic stage when spontaneous healing has not occurred. Tears of the biceps tendon anchor are unlikely to heal without treatment because the biceps constantly pulls on the labrum.
Chronic tears may require surgery if patients are unwilling or unable to modify their activities sufficiently to allow for healing and comfort. Surgery should be considered if:
- pain is unresponsive to anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen, rest, and activity modification.
- the labrum has not healed after an acute injury.
Arthroscopic treatment is the standard of practice for most labral injuries not associated with instability. The majority of these can be treated with simple debridement (removal of abnormal, damaged, or excess tissue). This procedure will eliminate flaps that may impinge the movement of the humerus on the glenoid and/or remove any unstable portion of the labrum.
Certain painful and unstable SLAP tears, in which the biceps is detached, need special attention. If the biceps tendon anchor is no longer firmly attached to the glenoid, it must be re-attached to the bone. The surgeon uses suture anchors and /or arthroscopic knot tying techniques to repair the torn labrum of younger patients.
It is often safer for older individuals to have a debridement of the labrum and a biceps tenodesis. A tenodesis is a procedure in which the biceps is repaired to the bone outside the glenohumeral joint to relieve pain, yet allow it to retain some strength and function. This procedure can be a good choice for older patients because the blood supply to the labrum diminishes with age, making the healing process more difficult. The decision to perform a tenodesis repair should be made by the doctor and patient together, after a thorough discussion of the surgical options and the healing process.
What types of complications can occur?
Complications associated with surgery for labral tears are few:
- The risk of infection in arthroscopic procedures is extremely low and can be a complication of any surgical procedure.
- Stiffness after surgery is unlikely since debridement allows early arm movement. Physical therapy will usually relieve stiffness resulting from the sling that is needed for four or more weeks for labral repairs.
- Failure of healing can occur due to technique, biology, or the patient's unwillingness to follow post-operative instructions and the prescribed rehabilitation program.
RECOVERY
In the early recovery period, physical therapy to regain hand and elbow range of motion can begin immediately. Labral tears that require only debridement are allowed early range of motion and physical therapy to prevent stiffness.
Labral injuries that involve repair or tenodesis of the biceps tendon require a period of immobilization to allow the tendon to heal back to bone. After approximately four weeks of sling immobilization, physical therapy may begin.
Overhead athletes with SLAP repairs can expect a substantial delay before they can resume throwing. It usually takes about six months for the patient to regain full endurance and throwing velocity.
- Sutures are removed seven to ten days after surgery and showering can resume.
- Shoulder range of motion exercises after a biceps repair begin approximately six weeks after surgery, when the healing process is complete.
Labral injuries that involve repair or tenodesis of the biceps tendon require a period of immobilization to allow the tendon to heal back to bone. After approximately four weeks of sling immobilization, physical therapy may begin.
Overhead athletes with SLAP repairs can expect a substantial delay before they can resume throwing. It usually takes about six months for the patient to regain full endurance and throwing velocity.
FAQs
Will a labral tear heal without treatment?
There are no good natural history studies on labral injuries. There are acute (sudden) labral tear injuries that are likely to heal without surgery. In chronic (longstanding) cases, however, there are no successful non-operative treatments.
What are the causes of a SLAP tear?
The causes of SLAP tears are a subject of debate among orthopaedic surgeons. There are several injury patterns that can lead to a tear. The most common causes are thought to be:
The decision to perform a tenodesis is based upon the location of the tear, the amount of biceps involved, and the quality of the remaining tendon. The more degenerative the tissue, the more likely it is that a tenodesis will be a successful treatment. The patient's age is a secondary concern, but is a factor (along with the other variables) that should be considered when assessing the likelihood of success of a primary repair versus the results obtainable with a tenodesis.
References
There are no good natural history studies on labral injuries. There are acute (sudden) labral tear injuries that are likely to heal without surgery. In chronic (longstanding) cases, however, there are no successful non-operative treatments.
What are the causes of a SLAP tear?
The causes of SLAP tears are a subject of debate among orthopaedic surgeons. There are several injury patterns that can lead to a tear. The most common causes are thought to be:
- a fall on the outstretched hand that drives the humerus upward and causes the superior labrum to tear.
- a sudden and often unexpected load applied to the biceps, which can cause a tear.
- extremes of external rotation and abduction (movement away from the body) during throwing that causes the labrum to "peel back" from its attachment.
The decision to perform a tenodesis is based upon the location of the tear, the amount of biceps involved, and the quality of the remaining tendon. The more degenerative the tissue, the more likely it is that a tenodesis will be a successful treatment. The patient's age is a secondary concern, but is a factor (along with the other variables) that should be considered when assessing the likelihood of success of a primary repair versus the results obtainable with a tenodesis.
References